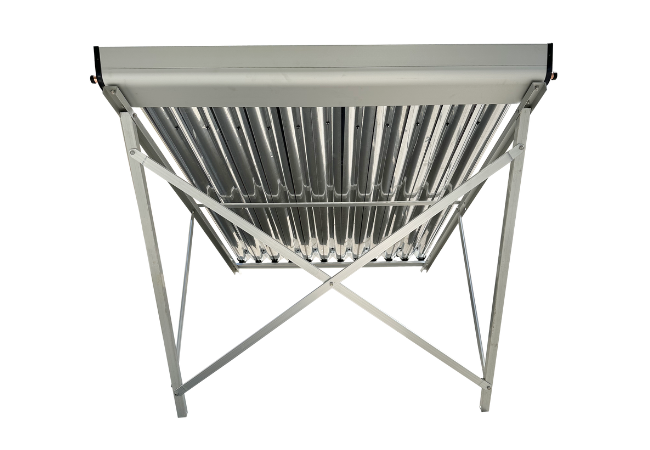
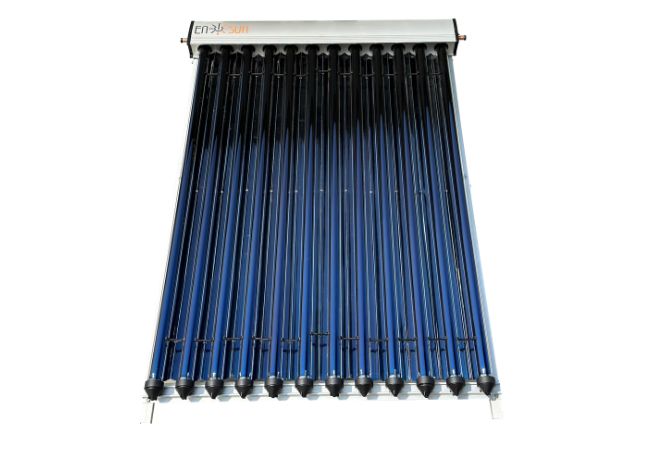
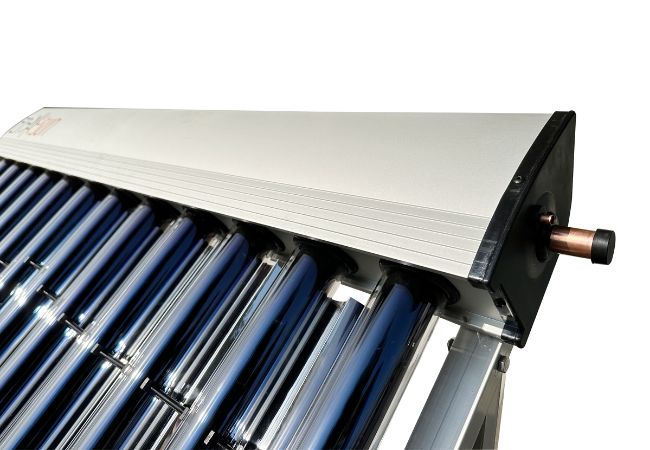
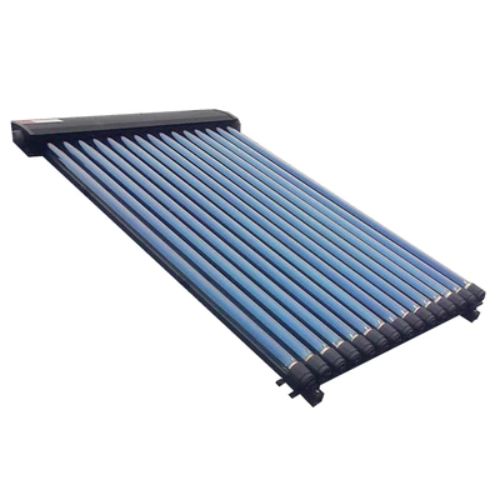
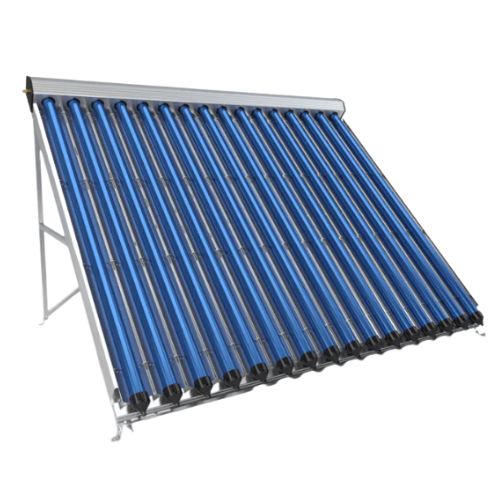
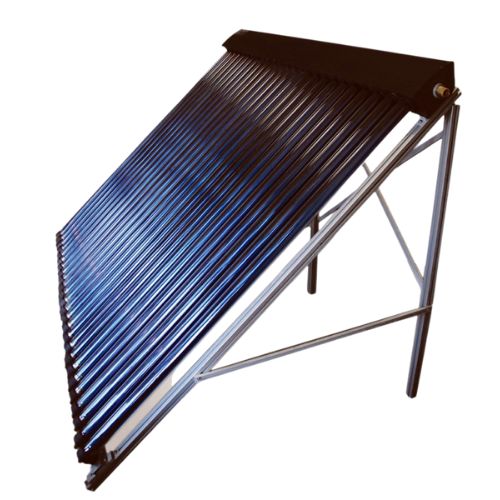
Ensun-CPC Solar Collector
The Ensun CPC solar collector is a heat pipe solar collector with a CPC reflector. CPC reflector maximum performance at minimum dimensions of heat pipe solar collector. CPC reflector can enlarge the absorbing area of the vacuum tube from 180 degrees to 360 degrees. The power output could be 50% higher compared to a solar collector without a CPC reflector.
- 50% higher preformance
- Easy assemble CPC reflector
- 360°sunlight absorber
- Temperature startup faster than the normal solar thermal collectors
- More thermal output for same size of collector
- Ideal solution for heat project
Leading CPC Solar Collector Manufacturer
Ensun CPC solar collectors are composed of air and waterproof design collector tray, high-selective coated copper absorber, and solar safety glass. It also designed with a galvanically anodized pure aluminium reflector, UV protected special seal, aluminium glass holding strip and other parts. The components are made from high-quality and weather-resistant materials.
Ensun manufactures CPC solar collectors in a variety of sizes to suit your needs. Our products have a 25-year system lifespan. It is capable of meeting at least 70% of home hot water demands. These withstand different harmful environmental conditions such as snow loads, dirt, UV radiation, wind, rain, dirt, high temperatures, etc. Excellent investment in the future of home and the environment.
To satisfy your needs, Ensun offer full customization of your orders. Different design and colors are available for sheet metal flashings and frame profiles production. You can send your design and ideas. We will help you create your OEM products to skyrocket your business.
Wide Range of Installations
Our range of CPC solar collectors are available in various installations. It includes:
- Roof-integrated mounting
- Installation on a flat roof with gravel box
- Installation on a flat roof with a concrete base
- On-roof mounting – parallel 0°
- On-roof mounting -elevated
- Façade installations
- Free standing
We also offer special designs and installations available on request.

The primary elements influencing solar collector performance:
- collector’s area
- absorber plate temperature
- collector tilt angle
- the number of glass covers
- absorber absorptivity and emissivity
- an emissivity of the glass cover
For most households, the best angle for solar panel installation is close to or equal to home’s latitude. This angle is usually between 30° and 45°.
Related Product
CPC Solar Collector
A compound parabolic concentrator solar collector is a major solar collector type whose capture of sunlight is utilized for heating. It consists of a reflector in a curved trough shape that focuses sunlight onto a receiver tube located along the reflector’s focal line.
The unique reflector design allows the collector to capture and concentrate sunlight over a wide range of angles improving efficiency. In these tubes there are transfer fluids that transfer sunlight energy in heat form.
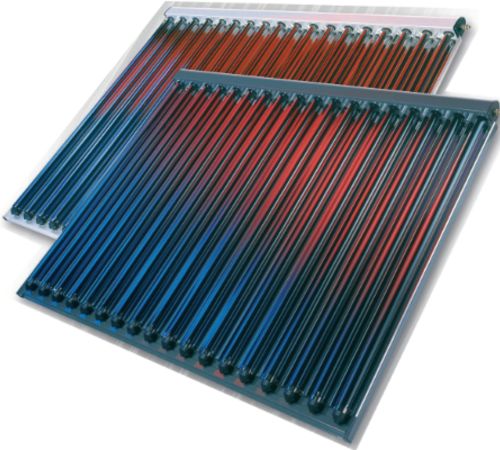

Components of CPC Solar Collector
A compound parabolic concentrator solar collector consists several key components configured according to the design, application, size, and efficiency requirements.
These components include:
- Reflector: It is the primary component used to capture and focus sunlight onto the receiver tube. It is made of highly reflective materials and shaped like a trough with a side pairing of parabolic curves and base compound curve.
- Receiver Tube: It is a cylindrical tube made highly thermally conductive material, positioned along the focal line of the reflector. It contains a heat transfer fluid that heats up on absorbing the concentrated sunlight.
- Insulation: Insulating materials reduce thermal losses improving the overall system efficiency and are applied to the collector sides and back. Insulation also helps maintain the working fluid’s temperature preventing heat escape.
- Support Structure: Constructed from sturdy materials like metal or composite, the support structure holds the reflector in place providing stability.
- Tracking Mechanism: Some of these solar collectors have a tracking mechanism that follows the sun’s movement across the sky improving overall efficiency. This system can be manual or automated and adjusts the reflector orientation, ensuring optimal sunlight capture throughout the day.
- Fluid Circulation System: Is a pipe, pump, and valve system that helps circulate the working fluid. It is necessary for the transfer of absorbed heat by the working fluid to the desired application.
Benefits of CPC Solar Collector
There are several merits to employing compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors for your heating applications as follows:
i. Durability: The materials used to make these solar collectors are resistant to environmental factors such as UV radiation and weathering. As such, they provide reliable and sustainable performance over an extended period.
ii. High Efficiency: The unique geometry of the reflector allows for effective sunlight concentration resulting in higher energy collection and conversion. As a result, higher temperatures of the working fluid are achieved.
iii. Versatility: Compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors find multiple uses in solar thermal applications such as water, space and industrial process heating. Their versatility also allows for integration with different systems and technologies like heat exchangers and photovoltaic cells to create hybrid systems.
iv. Wide Acceptance Angle: The reflector design enables sunlight capture from a wide range of incident angles throughout the day maximizing collection. This allows for maximum sunlight capture and even when the sun is not directly perpendicular to the collector improving performance.
v. Environmental Benefits: Compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors harness solar energy which is a clean and renewable energy source. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a more sustainable environment.
Working Principle of a CPC Solar Collector
Solar collectors employing the compound parabolic concentrator design, can effectively capture and concentrate sunlight, maximizing energy conversion efficiency. The working principle of a compound parabolic concentrator solar collector involves the following key steps:
Sunlight Capture
This occurs on the reflector, shaped like a trough with parabolic curve sides pairing and a compound curve bottom. This shape allows for the capture sunlight over a wide range of angles throughout the day. The reflector is made of highly reflective materials, maximizing the reflection of sunlight onto the receiver tube.
Concentration of Sunlight
The sunlight striking the reflector is reflected and directed towards the reflector’s focal line. Its unique geometry ensures the sunlight is concentrated and focused onto the receiver tube with minimum reflection loss of sunlight.
Receiver Tube
The receiver tube is a cylindrical tube consisting highly thermally conductive material like copper positioned along the reflector’s focal line. It contains a stationary fluid or flowing through the tube in a continuous loop depending on the collector design. The fluid is usually water or heat transfer oil, and takes up the focused sunlight increasing its thermal energy.
Heat Transfer
When the heat transfer fluid is subjected to the focused sunlight, it increases its thermal capacity and temperature. The now energetic fluid is transferred for either direct use or further thermal energy treatment by subjecting it to an exchanger. The contained thermally energy is then put to use in a rnage of applications.
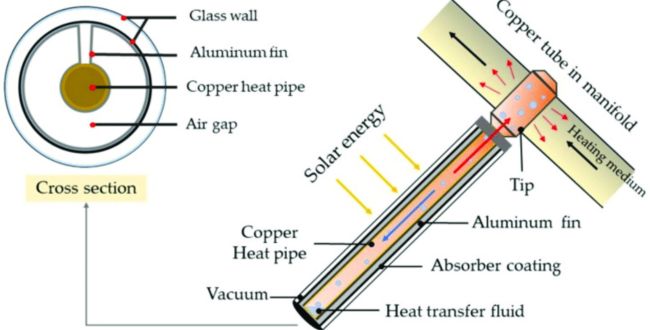
Design Considerations of a CPC Solar Collector
Proper design of compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors leads to improved performance and efficiency in solar thermal applications. Some key design considerations for these solar collectors include:
Construction
The shape and geometry of the compound parabolic concentrator solar collector’s reflector is crucial for efficient sunlight capture and concentration. The reflector features two parabolic curves on the sides alongside a compound curve at the bottom.
The parabolic curve focuses sunlight onto the receiver tube. On the other hand, the compound curve ensures sunlight capture is over a wide range of angles throughout the day.
Reflective Materials
The reflector surface needs high reflectivity to maximize the reflection of sunlight onto the receiver tube utilizing polished metal or mirrors. The design of the reflector should also be such that it minimizes absorption/reflective losses.
Positioning of Receiver Tube
The receiver tube is typically positioned along the reflector’s focal line at an optimum distance that ensures maximum sunlight concentration. Proper alignment and receiver tube positioning are critical to high thermal efficiency achievement.
Design of Receiver Tube
The receiver tube design should allow efficient absorption and transfer of concentrated solar energy to the working fluid. The thermal conductivity of the tube material should be high, as well as the working fluid’s to facilitate efficient heat transfer.
Insulation
Insulation efforts are necessary to thwart heat loss via conduction and convection to the surrounding from the collector structure. Effective insulation helps in maintaining the temperature of the working fluid thereby enhancing collector performance.
Tracking Mechanism
A tracking mechanism optimizes solar energy capture throughout the day allowing the collector to follow the sun’s movement across the sky. This ensures the reflector is always aligned with the sun’s position, maximizing the amount of sunlight captured.
Types of CPC Solar Collector
Compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors can be designed to meet specific requirements. The choice of the collector type depends on different factors such as the intended use and design.
Linear-Focusing
Linear-focusing compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors focus the received sunlight onto a tube ideally located along the collector’s line of focus. This type finds use in solar water and space heating systems.
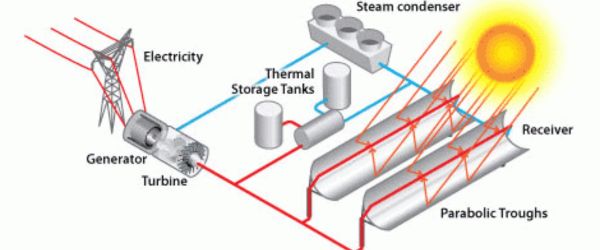
Point-Focusing
These solar collectors concentrate sunlight onto a single point with a reflector shape featuring a more pronounced parabolic curve base. Directing the concentrated sunlight onto a small receiver allows use in applications requiring high temperatures.

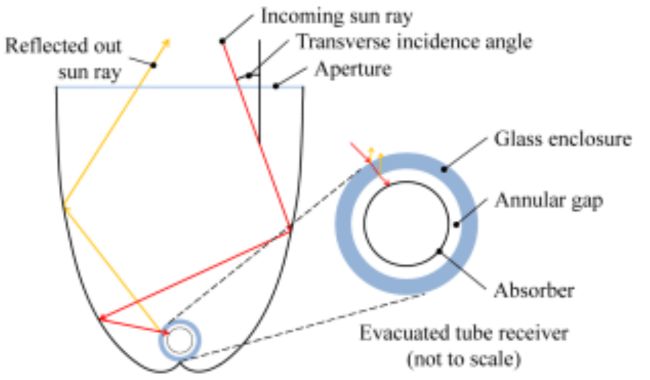
CPC Solar Collector Efficiency
The efficiency of a compound parabolic concentrator solar collector refers to its ability to effectively convert sunlight into usable thermal energy. Overall efficiency is influenced by the design and operating conditions including external factors like climate and irradiation.
The efficiency of compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors typically ranges between 40% to 70% and can be classified as follows:
- Optical Efficiency: This measures how effectively the compound parabolic concentrator solar reflector captures and concentrates sunlight onto the receiver tube. It is influenced by the reflector design, reflective materials, and the reflector surface condition.
- Thermal Efficiency: This is determined as the collector’s success in transferring collected energy form sunlight into heat absorbable by the heat transfer fluid. It is dependent on factors like the receiver tube design and material, and working fluid characteristics.
- Tracking Efficiency: Where there’s a tracking mechanism, the tracking efficiency is determined by the success in following the sun’s movement across the sky. This requires the collector to maintain optimal alignment with the sunlight maximizing the amount of sunlight captured.
Limitations of CPC Solar Collector
While compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors offer several advantages, they are encumbered with some limitations mentioned thus:
- Cost: Installing compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors can cost more compared to other solar collectors and conventional thermal sources. Overall factors influencing cost include the complex reflector design and quality reflective materials.
- Limited Concentration Ratio: Compared to similar solar collectors like dish concentrators, these collectors have a typically lower concentration ratio. This ratio determines the amount of sunlight focused onto the receiver tube.
- Limited Tracking: The fixed geometry of compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors is incapable of direct solar tracking without using an external mechanism. As a result, this increases the design complexity and adds to the cost.
- Maintenance: Frequent cleaning of the reflector surface is necessary to keep it free from dirt or dust that can obstruct sunlight. Obstruction of sunlight reduces the optical efficiency resulting in a reduced thermal performance.
- Restricted Thermal Energy Range: These solar collectors are incapable of high temperature applications mostly suitable for low to medium temperature applications. Where high-temperatures are required, alternatives such as solar towers or a combination with such is necessary.
- Sensitivity to Misalignment: Even slight deviations from optimal alignment with the sun can significantly reduce the efficiency of compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors. Therefore, in order to maximize performance, it is vital to ensure proper installation and alignment of the collector.
- Space Requirement: For these collectors to achieve the desired concentration and efficiency, they generally require a larger surface area compared to other solar collectors. As a result, their use may be limited where space is restricted.
Uses of CPC Solar Collector
The versatility of compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors makes them suitable for a range of solar thermal systems. Their flexibility and efficiency contributes to sustainable energy solutions, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
Some common uses of these solar collectors are discussed below:
i. Industrial Process Heating: Various manufacturing processes often require high-temperature heat for food processing, textile treatment, chemical preparations, and sintering pharmaceuticals. The high concentration capability of compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors allows for the generation of such high-temperature heat.
ii. Cooking: Compound parabolic concentrator solar cookers can be utilized to concentrate sunlight for cooking by focusing sunlight onto a cooking vessel. This eliminates the need for traditional fuel sources allowing efficient and clean cooking particularly where alternative fuel sources are limited.
iii. Cooling: Integration of these solar collectors into solar cooling systems allows for utilization of the collected thermal energy for cooling purposes. The concentrated sunlight is converted into thermal energy used in adsorption cooling process thereby reducing electricity consumption incurred by conventional cooling systems.
iv. Desalination: Solar desalination utilizes compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors in the conversion of saline water into freshwater. Utilizing the solar collector’s thermal energy reduces the energy requirements of the desalination process.
v. Water Heating: Solar water heating systems use these solar collectors to concentrate sunlight for the direct or indirect heating of water. This is useful for both domestic and commercial applications garnering energy savings.
vi. Space Heating: These collectors can circulate the heat transfer fluid through a radiant heating system providing alternative heat for buildings. They can also be integrated with heat exchangers for a forced-air heating system contributing to energy savings from going green.
Conclusion
Compound parabolic concentrator solar collectors continue to be a valuable option for various solar thermal applications. With proper design, installation, and maintenance, their efficiency and effectiveness can be optimized to harness solar energy and contribute to sustainable energy solutions.